Hello Friend.
Here is an example to demonstrate the principle of building models in zencad.
from zencad import *
a = box(200, 200, 200, center = True)
b = sphere(120)
c = sphere(60)
model = a - b + c
display(model)
show()
What's happening:
from zencad import *
In the first line, we import into the current zencad namespace. In this case, we are interested in the box,sphere, display,show functions.
a = box(200, 200, 200, center = True)
b = sphere(120)
c = sphere(60)
Preparing geometric primitives. A box object is created with dimensions 200x200x200 and an offset of the geometric center to the origin. It also creates two spheres with a radius of 120 and 60.
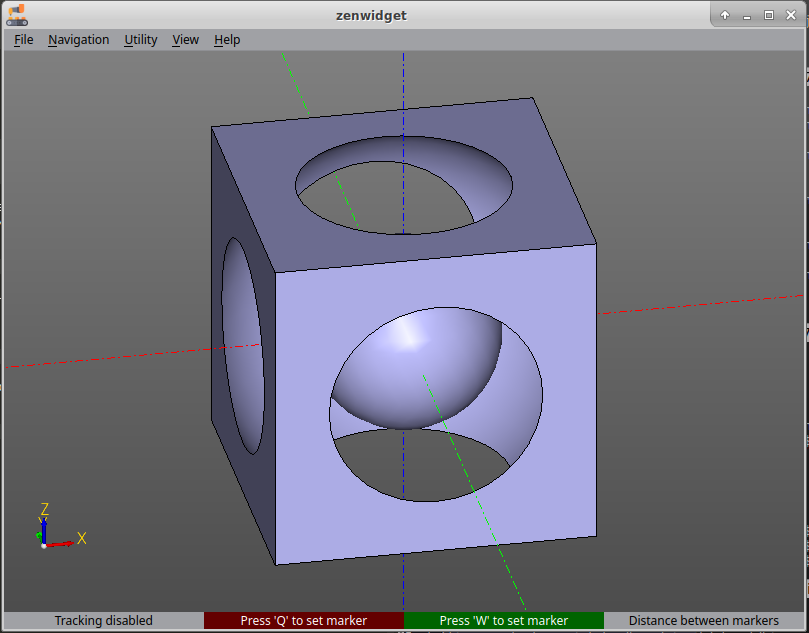
model = a - b + c
Computing the model using boolean operations. First, a large sphere will be subtracted from the cube. Then a small one was added. The order of the terms is important in this case, since the operations of union and difference of geometric bodies are non-commutative.
disp(model)
The disp function passes the object into the scene for later display.
show()
Displaying the scene widget.
If everything went well: